Abstract
Objectives
The objective of this study was to compare the diagnostic performance of direct C-arm flat panel computed tomography arthrography (FPCT-A) with direct magnetic resonance arthrography (MR-A) of the wrist in patients with clinically suspected pathologies.
Methods
Forty-nine patients underwent tri-compartmental wrist arthrography. FPCT-A was acquired using a high-resolution acquisition mode, followed by a 3-T MR exam using a dedicated wrist coil. Image quality and artifacts of FPCT-A and MR-A were evaluated with regard to the depictability of anatomical structures. The time stamps for the different image acquisitions were recorded for workflow assessment.
Results
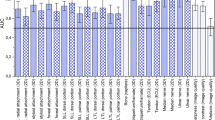
Image quality was rated significantly superior for all structures for FPCT-A (p < 0.001) as compared to MR-A including intrinsic ligaments, TFCC, cartilage, subchondral bone, and trabeculae. The differences in image quality were highest for cartilage (2.0) and lowest for TFCC (0.9). The artifacts were rated lower in MR-A than in FPCT-A (p < 0.001). The procedure was more time-efficient in FPCT-A than in MR-A.
Conclusions
FPCT-A of the wrist provides superior image quality and optimized workflow as compared to MR-A. Therefore, FPCT-A should be considered in patients scheduled for dedicated imaging of the intrinsic structures of the wrist.
Key Points
• FPCT arthrography allows high-resolution imaging of the intrinsic wrist structures.
• The image quality is superior as compared to MR arthrography.
• The procedure is more time-efficient than MR arthrography.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAP:
-
Dose-area product
- DRUJ:
-
Distal radioulnar joint
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- FPCT:
-
Flat panel computed tomography
- MDCT:
-
Multidetector computed tomography
- MJ:
-
Midcarpal joint
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance arthrography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- LTL:
-
Lunotriquetral ligament
- PDw:
-
Proton density weighted
- RC:
-
Radiocarpal joint
- SLL:
-
Scapholunate ligament
- TE:
-
Echo time
- TFCC:
-
Triangular fibrocartilage complex
- TR:
-
Repetition time
- TSE:
-
Turbo spin echo
References
Kümmel A, Ebner L, Kraus M et al (2014) Magnet resonance imaging in common injuries of the wrist. Unfallchirurg 117:221–226
Rohman EM, Agel J, Putnam MD, Adams JE (2014) Scapholunate interosseous ligament injuries: a retrospective review of treatment and outcomes in 82 wrists. J Hand Surg Am 39:2020–2026
Magee T (2009) Comparison of 3-T MRI and arthroscopy of intrinsic wrist ligament and TFCC tears. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:80–85
Smith TO, Drew B, Toms AP, Jerosch-Herold C, Chojnowski AJ (2012) Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance arthrography for triangular fibrocartilaginous complex injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94:824–832
Štouračová A, Šprláková-Puková A, Čižmář I, Procházková J, Janoušová E, Vališ P (2016) High-resolution MR examination of the scapholunate ligament using a microscopic coil: comparison with direct MR arthrography and arthroscopy findings. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech 83:327–331
Moser T, Dosch JC, Moussaoui A, Dietemann JL (2007) Wrist ligament tears: evaluation of MRI and combined MDCT and MR arthrography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:1278–1286
Schmid MR, Schertler T, Pfirrmann CW et al (2005) Interosseous ligament tears of the wrist: comparison of multi-detector row CT arthrography and MR imaging. Radiology 237:1008–1013
Fischer W, Bohndorf K, Kreitner KF, Schmitt R, Wörtler K, Zentner J (2009) Indications for CT and MR arthrography--recommendations of the musculoskeletal workgroup of the DRG. Rofo 181:441–446
Guggenberger R, Fischer MA, Hodler J, Pfammatter T, Andreisek G (2012) Flat-panel CT arthrography: feasibility study and comparison to multidetector CT arthrography. Invest Radiol 47:312–318
Kyriakou Y, Struffert T, Dörfler A, Kalender WA (2009) Basic principles of flat detector computed tomography (FD-CT). Radiologe 49:811–819
Guggenberger R, Morsbach F, Alkadhi H et al (2013) C-arm flat-panel CT arthrography of the wrist and elbow: first experiences in human cadavers. Skeletal Radiol 42:419–429
irr: Various coefficients of interrater reliability and agreement version 0.84 from CRAN. https://rdrr.io/cran/irr/. Accessed 21 Oct 2018
McHugh ML (2012) Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochem Med (Zagreb) 22:276–282
Robinson G, Chung T, Finlay K, Friedman L (2006) Axial oblique MR imaging of the intrinsic ligaments of the wrist: initial experience. Skeletal Radiol 35:765–773
Lee RK, Ng AW, Tong CS et al (2013) Intrinsic ligament and triangular fibrocartilage complex tears of the wrist: comparison of MDCT arthrography, conventional 3-T MRI, and MR arthrography. Skeletal Radiol 42:1277–1285
Daenen BR, Ferrara MA, Marcelis S, Dondelinger RF (1998) Evaluation of patellar cartilage surface lesions: comparison of CT arthrography and fat-suppressed FLASH 3D MR imaging. Eur Radiol 8:981–985
El-Khoury GY, Alliman KJ, Lundberg HJ, Rudert MJ, Brown TD, Saltzman CL (2004) Cartilage thickness in cadaveric ankles: measurement with double-contrast multi-detector row CT arthrography versus MR imaging. Radiology 233:768–773
Sahin M, Calisir C, Omeroglu H, Inan U, Mutlu F, Kaya T (2014) Evaluation of labral pathology and hip articular cartilage in patients with femoroacetabular impingement (FAI): comparison of multidetector CT arthrography and MR arthrography. Pol J Radiol 79:374–380
Acid S, Le Corroller T, Aswad R, Pauly V, Champsaur P (2012) Preoperative imaging of anterior shoulder instability: diagnostic effectiveness of MDCT arthrography and comparison with MR arthrography and arthroscopy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198:661–667
Sutherland JK, Nozaki T, Kaneko Y et al (2016) Initial experience with 3D isotropic high-resolution 3 T MR arthrography of the wrist. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-016-0890-5
Guggenberger R, Winklhofer S, Spiczak JV, Andreisek G, Alkadhi H (2013) In vitro high-resolution flat-panel computed tomographic arthrography for artificial cartilage defect detection: comparison with multidetector computed tomography. Invest Radiol 48:614–621
Werncke T, Sonnow L, Meyer BC et al (2017) Ultra-high resolution C-arm CT arthrography of the wrist: radiation dose and image quality compared to conventional multidetector computed tomography. Eur J Radiol 89:191–199
Chemouni D, Champsaur P, Guenoun D, Desrousseaux J, Pauly V, Le Corroller T (2014) Diagnostic performance of flat-panel CT arthrography for cartilage defect detection in the ankle joint: comparison with MDCT arthrography with gross anatomy as the reference standard. AJR Am J Roentgenol 203:1069–1074
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is PD Dr. von Falck.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• observational
• performed at one institution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonnow, L., Koennecker, S., Luketina, R. et al. High-resolution flat panel CT versus 3-T MR arthrography of the wrist: initial results in vivo. Eur Radiol 29, 3233–3240 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5901-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5901-5